Chem 221: Organic Chemistry I (Bennett) Lecture Textbook
Stereospecific and stereoconvergent nucleophilic substitution reactions at tertiary carbon centers – ScienceDirect
8: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions

Source Image: en.wikipedia.org
Download Image
Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.

Source Image: homework.study.com
Download Image
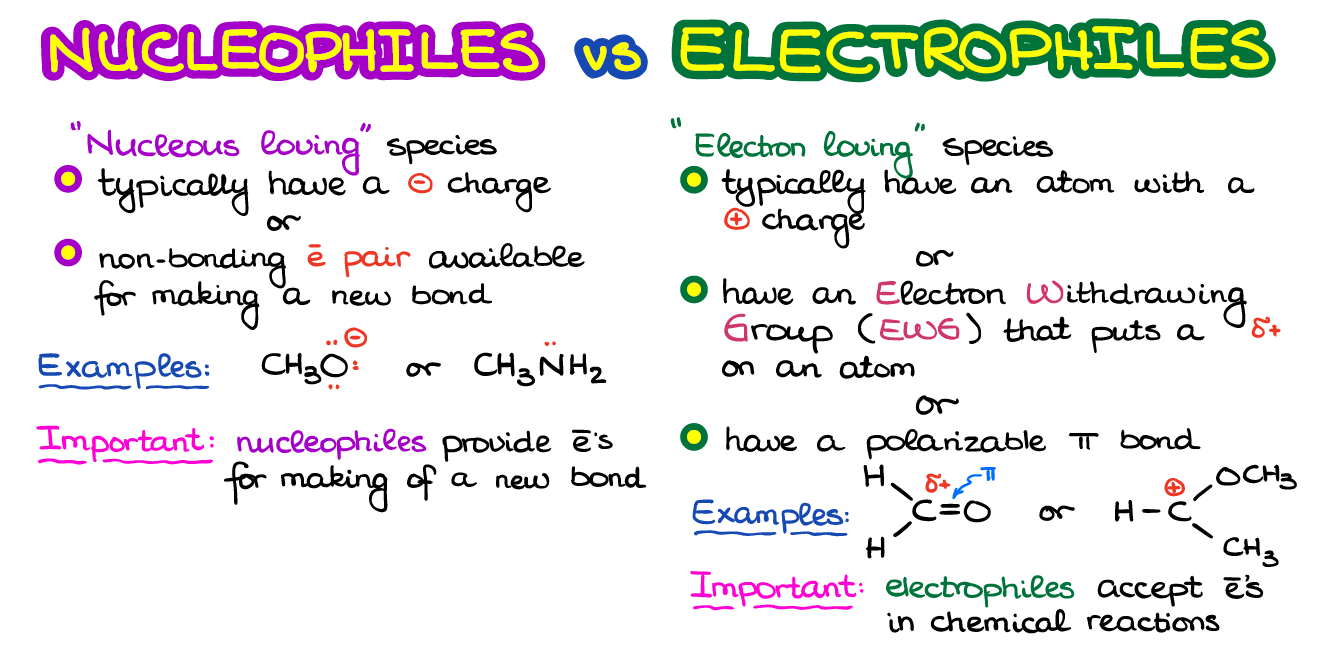
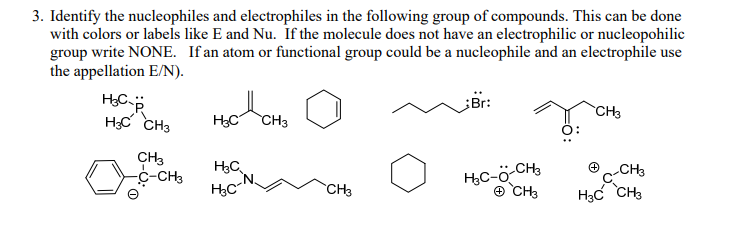
Solved 3. Identify the nucleophiles and electrophiles in the | Chegg.com 235 Question 2b Textbook Question In each reaction, label the reactants as Lewis acids (electrophiles) or Lewis bases (nucleophiles). Use curved arrows to show the movement of electron pairs in the reactions. Draw any nonbonding electrons to show how they participate in the reactions. b. (CH3)2NH + CH3Cl —> (CH3)3 (+NH) + Cl- 246 Question 2c
Source Image: organicchemistrytutor.com
Download Image
Identify The Nucleophile In The Following Reaction
235 Question 2b Textbook Question In each reaction, label the reactants as Lewis acids (electrophiles) or Lewis bases (nucleophiles). Use curved arrows to show the movement of electron pairs in the reactions. Draw any nonbonding electrons to show how they participate in the reactions. b. (CH3)2NH + CH3Cl —> (CH3)3 (+NH) + Cl- 246 Question 2c Rank the following compounds in order of increasing nucleophilicity. Ammonia is a stronger nucleophile than water because nitrogen is electronegative than oxygen. What this means is that the nitrogen-bound lone pair of ammonia is more loosely contained than the oxygen-bound lone pairs of water. As a result, they are more easily donated to form
Electrophiles and Nucleophiles — Organic Chemistry Tutor
Electrophiles. In the vast majority of the nucleophilic substitution reactions you will see in this and other organic chemistry texts, the electrophilic atom is a carbon which is bonded to an electronegative atom, usually oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or a halogen. The concept of electrophilicity is relatively simple: an electron-poor atom is an Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction – Definition, Types, Mechanisms, Examples And Comparison

Source Image: byjus.com
Download Image
Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equations as nucleophiles – YouTube Electrophiles. In the vast majority of the nucleophilic substitution reactions you will see in this and other organic chemistry texts, the electrophilic atom is a carbon which is bonded to an electronegative atom, usually oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or a halogen. The concept of electrophilicity is relatively simple: an electron-poor atom is an

Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
Stereospecific and stereoconvergent nucleophilic substitution reactions at tertiary carbon centers – ScienceDirect Chem 221: Organic Chemistry I (Bennett) Lecture Textbook

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Solved 3. Identify the nucleophiles and electrophiles in the | Chegg.com Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Solved Identify the nucleophile in the following reaction. | Chegg.com Identify the nucleophile and the electrophile in the following acid-base reactions: a. b. Skip to main content. Organic Chemistry. Start typing, then use the up and down arrows to select an option from the list. … Identify the nucleophile and the electrophile in the following acid-base reactions: a. b. Verified Solution. 5m.

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
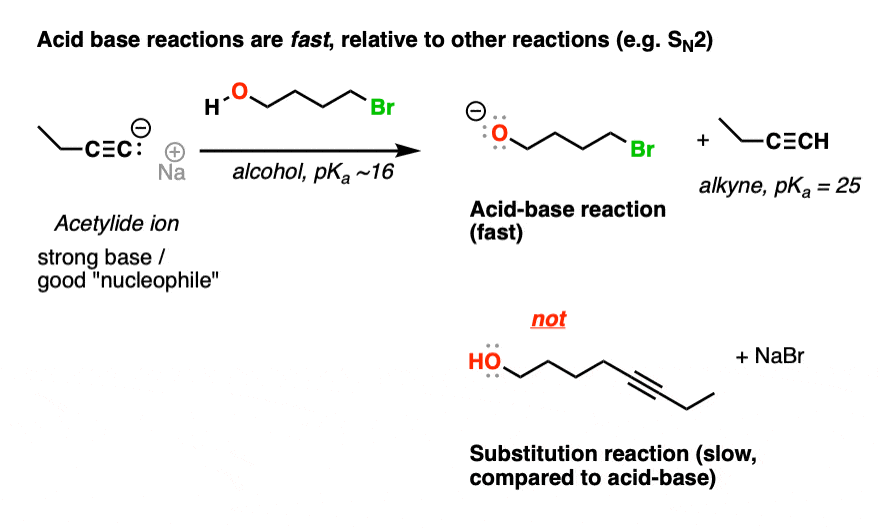
Acid-Base Reactions Are Fast (Compared To Substitution And Addition) 235 Question 2b Textbook Question In each reaction, label the reactants as Lewis acids (electrophiles) or Lewis bases (nucleophiles). Use curved arrows to show the movement of electron pairs in the reactions. Draw any nonbonding electrons to show how they participate in the reactions. b. (CH3)2NH + CH3Cl —> (CH3)3 (+NH) + Cl- 246 Question 2c
Source Image: masterorganicchemistry.com
Download Image
HW | PDF | Chemical Reactions | Chemical Compounds Rank the following compounds in order of increasing nucleophilicity. Ammonia is a stronger nucleophile than water because nitrogen is electronegative than oxygen. What this means is that the nitrogen-bound lone pair of ammonia is more loosely contained than the oxygen-bound lone pairs of water. As a result, they are more easily donated to form

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equations as nucleophiles – YouTube
HW | PDF | Chemical Reactions | Chemical Compounds 8: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions
Solved 3. Identify the nucleophiles and electrophiles in the | Chegg.com Acid-Base Reactions Are Fast (Compared To Substitution And Addition) Identify the nucleophile and the electrophile in the following acid-base reactions: a. b. Skip to main content. Organic Chemistry. Start typing, then use the up and down arrows to select an option from the list. … Identify the nucleophile and the electrophile in the following acid-base reactions: a. b. Verified Solution. 5m.